
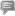 0 Comment(s)
0 Comment(s) Print
Print E-mail China.cn, April 22, 2025
E-mail China.cn, April 22, 2025Editor's note: Guqin, a plucked seven-string zither, is one of the oldest and most revered traditional Chinese musical instruments. Known for its refined sound and deep cultural symbolism, the Guqin has been an essential part of Chinese cultural life for over three millennia.

In 2008, it was inscribed on the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. The Guqin is celebrated not only for its distinctive, meditative sound but also for its close association with Chinese philosophy, poetry and calligraphy.
The origins of Guqin date back over 3,000 years. It has long been associated with Confucian values and the cultivation of moral character. Guqin was one of the four arts — along with calligraphy, painting and an ancient form of chess — that Chinese scholars were expected to master. Throughout the dynasties, it became a symbol of inner harmony, reflection and the spiritual quest of the literati class.
Guqin music is known for its quiet, subtle tones and wide range of expressive techniques. Its repertoire includes a mixture of ancient melodies — some dating back hundreds or even thousands of years — and more recent compositions. The instrument's playing techniques, such as sliding, plucking and harmonics, allow the performer to express complex emotions and philosophical ideas. Many Guqin pieces are linked with nature or friendship themes, such as "Running Water" and "Yangguan Sandie (Parting for Yangguan)."
Guqin playing developed as an elite art form, practiced by noblemen and scholars in intimate settings, and was therefore never intended for public performance.
In the 20th century, the Guqin faced significant challenges due to the changes of the times. The number of Guqin players and masters declined sharply, and many ancient instruments and manuscripts were lost.
However, recent decades have seen a revival of interest in the Guqin, both within China and internationally. Conservatories, cultural institutions, and independent scholars have worked to preserve and promote Guqin music through performances, recordings, academic research and education. Young people are increasingly drawn to the instrument as a symbol of cultural identity and spiritual depth.
Today, Guqin societies operate across China and abroad, organizing workshops, concerts and gatherings. Efforts have also been made to digitize ancient manuscripts and incorporate Guqin education into school curricula. Despite these positive developments, the tradition remains vulnerable due to its complexity, the limited number of skilled masters, and the challenge of maintaining traditions in a modernized society.
In recognizing the art of Guqin music, UNESCO highlighted its historical importance, artistic value and philosophical depth. The organization noted that Guqin music reflects key elements of traditional Chinese culture, including Confucianism, Taoism and Buddhism. Its meditative nature promotes introspection and harmony between people and the natural world.
UNESCO also emphasized the need to preserve Guqin's traditional transmission and craftsmanship methods, as well as to support efforts that ensure its continued practice and relevance in the modern era. The designation as Intangible Cultural Heritage aims to encourage both governmental and community support to preserve this extraordinary tradition for future generations.
Discover more treasures from China on UNESCO's ICH list:
? 2024: Spring Festival
? 2022: Traditional tea processing
? 2020: Wangchuan ceremony, taijiquan
? 2018: Lum medicinal bathing of Sowa Rigpa
? 2016: Twenty-four solar terms
? 2013: Abacus-based Zhusuan
? 2012: Training plan for Fujian puppetry performers
? 2011: Shadow puppetry, Yimakan storytelling
? 2010: Peking opera, acupuncture and moxibustion, wooden movable-type printing, watertight-bulkhead technology of Chinese junks, Meshrep
? 2009: Yueju opera, Xi'an wind and percussion ensemble, traditional handicrafts of making Xuan paper, traditional firing techniques of Longquan celadon, Tibetan opera, sericulture and silk craftsmanship, Regong arts, Nanyin, Khoomei, Mazu belief and customs, Dragon Boat Festival, Manas, Craftsmanship of Nanjing Yunjin brocade, Xinjiang Uygur Muqam art, Hua'er, China engraved block printing technique, Chinese traditional architectural craftsmanship for timber-framed structures, Chinese paper-cut, Chinese calligraphy
? 2008: Kunqu opera

| 什么天喜地 | 邪淫是什么意思 | 什么思而行 | 100年前是什么朝代 | 抽动症是什么原因引起的 |
| 医院按摩挂什么科 | 琮字五行属什么 | 什么充电宝可以带上飞机 | 腰椎管狭窄吃什么药 | 一个田一个比读什么 |
| 千卡是什么意思 | 经常扁桃体发炎是什么原因 | 子宫病变有什么症状 | 心眼是什么意思 | 什么火海 |
| 糖尿病可以吃什么菜 | 宝宝吐奶是什么原因 | 免疫力低吃什么药 | 燃气是什么气体 | 孕妇脚肿是什么原因 |
| 算五行缺什么免费测试hcv9jop4ns8r.cn | 打啵什么意思bysq.com | 脊髓空洞是什么意思hcv7jop6ns7r.cn | 心下痞是什么意思hcv9jop3ns9r.cn | 点痣后需要注意什么事项hcv8jop1ns9r.cn |
| 晚上睡觉脚抽筋是什么原因引起的hcv8jop7ns5r.cn | 六月份是什么星座520myf.com | 谷氨酸高是什么原因hcv8jop6ns7r.cn | 澳大利亚位于什么板块hcv7jop4ns8r.cn | rom是什么意思hcv7jop5ns4r.cn |
| 手心脱皮是什么原因hcv7jop9ns7r.cn | 春饼卷什么菜好吃hcv9jop2ns5r.cn | 蓝莓树长什么样hcv8jop4ns9r.cn | zw是什么意思hcv9jop4ns5r.cn | 血浆是什么颜色hcv8jop5ns3r.cn |
| 玉皇大帝和王母娘娘是什么关系hcv9jop1ns4r.cn | 罢黜百家独尊儒术是什么意思hcv9jop3ns3r.cn | 每天吃黄瓜有什么好处hcv9jop4ns0r.cn | zro是什么牌子hcv9jop0ns3r.cn | 部队大校是什么级别hcv8jop9ns7r.cn |
Go to Forum >>0 Comment(s)